GWAS meta‑analysis of axial spondyloarthritis and Behçet’s disease identifies CXCR6 as a novel MHC‑I‑opathy gene in a Turkish population
Author: Dr. Mohammad Saeed
Dr. Mohammad Saeed is a member of the EULAR MHC-I-opathy group.
Read Full Text of the Article
“MHC-I-opathy” is a family of inflammatory disorders with a strong genetic link to HLA-I. These include Axial spondyloarthritis (AxSpA; previously Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) associated with HLA-B27), Behçet’s disease (BD; associated with HLA-B51) and psoriasis. Though the MHC-I genetic associations were discovered about 50 years ago, the pathogenesis of these disorders is not fully understood. To identify immunogenetic pathways for MHC-I-opathies, a cluster-based meta-analysis of AxSpA and BD Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) using OASIS was conducted. Both selected GWAS were from Turkiÿe for homogenous population effect.
OASIS (Objective Assimilation of SNPs Interacting in Synchrony) is a GWAS clustering algorithm, developed by Dr. Mohammad Saeed to identify genes of modest significance. These are often missed in classic analysis that use Manhattan plots to identify significant associations in GWAS. Clustering or binning methods, such as OASIS, increase power by decreasing the number of tests per study.
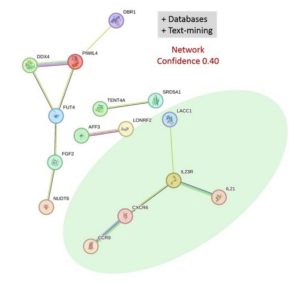
HLA-I was the only locus that was highly significant (P<1× 10–8) in both GWAS datasets. OASIS identified 234 independent modestly significant non-HLA loci in the two GWAS datasets (Bonferroni correction: P≤2.14×10⁻4; −log10 P≥3.67). The most signficant genes that this study identified were IL23R (1p31.3), LACC1 (13q14.11) and the novel CXCR6 (3p21.31). These are significantly associated with both AxSpA and BD. All three genes are down-regulated in these MHC-I-opathies. Protein interaction network showed that CXCR6 is part of the interactome of IL23R and LACC1 (P=0.00243). The novel gene, CXCR6, identified here codes for a G-protein coupled receptor expressed in several T-cell subsets and regulate their migration to tissues. A previous biological study showed that CXCR6+ CD8+ T-cells were actively recruited to psoriasis-affected skin. It also showed that TNF-α inhibition, which is part of the therapeutics (such as the biologic medications Eternacept, Adalimumab and Infliximab) for AxSpA and BD, reduced the CXCR6-mediated T-cell recruitment.
In summary, this study identified 15 loci common to both AxSpA and BD that may provide diagnostic and therapeutic targets for MHC-I-opathy. Major candidate genes for MHC-I-opathy identified here are IL23R, LACC1, and CXCR6. By integrating locus-level significance with functional validation in independent expression datasets, we ensured that only statistically robust and biologically relevant associations were highlighted, thereby strengthening the reliability and interpretability of our findings.

